实现HttpSession
HttpSession是Java Web App的一种机制,用于在客户端和服务器之间维护会话状态信息。
Session原理
当客户端第一次请求Web应用程序时,服务器会为该客户端创建一个唯一的Session ID,该ID本质上是一个随机字符串,然后,将该ID存储在客户端的一个名为JSESSIONID的Cookie中。与此同时,服务器会在内存中创建一个HttpSession对象,与Session ID关联,用于存储与该客户端相关的状态信息。
当客户端发送后续请求时,服务器根据客户端发送的名为JSESSIONID的Cookie中获得Session ID,然后查找对应的HttpSession对象,并从中读取或继续写入状态信息。
Session用途
Session主要用于维护一个客户端的会话状态。通常,用户成功登录后,可以通过如下代码创建一个新的HttpSession,并将用户ID、用户名等信息放入HttpSession:
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/login")
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String username = req.getParameter("username");
String password = req.getParameter("password");
if (loginOk(username, password)) {
// 登录成功,获取Session:
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
// 将用户名放入Session:
session.setAttribute("username", username);
// 返回首页:
resp.sendRedirect("/");
} else {
// 登录失败:
resp.sendRedirect("/error");
}
}
}
在其他页面,可以随时获取HttpSession并取出用户信息,然后在页面展示给用户:
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/")
public class IndexServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取Session:
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
// 从Session中取出用户名:
String username = (String) session.getAttribute("username");
if (username == null) {
// 未获取到用户名,说明未登录:
resp.sendRedirect("/login");
} else {
// 获取到用户名,说明已登录:
String html = "<p>Welcome, " + username + "!</p>";
resp.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter pw = resp.getWriter();
pw.write(html);
pw.close();
}
}
}
当用户登出时,需要调用HttpSession的invalidate()方法,让会话失效,这样,用户将重新回到未登录状态,因为后续调用req.getSession()将返回一个新的HttpSession,从这个新的HttpSession取出的username将是null。
HttpSession的生命周期
第一次调用req.getSession()时,服务器会为该客户端创建一个新的HttpSession对象;
后续调用req.getSession()时,服务器会返回与之关联的HttpSession对象;
调用req.getSession().invalidate()时,服务器会销毁该客户端对应的HttpSession对象;
当客户端一段时间内没有新的请求,服务器会根据Session超时自动销毁超时的HttpSession对象。
HttpSession接口
HttpSession是一个接口,Java的Web应用调用HttpServletRequest的getSession()方法时,需要返回一个HttpSession的实现类。
了解了以上关于HttpSession的相关规范后,我们就可以开始实现对HttpSession的支持。
首先,我们需要一个SessionManager,用来管理所有的Session:
public class SessionManager {
// 引用ServletContext:
ServletContextImpl servletContext;
// 持有SessionID -> Session:
Map<String, HttpSessionImpl> sessions = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// Session默认过期时间(秒):
int inactiveInterval;
// 根据SessionID获取一个Session:
public HttpSession getSession(String sessionId) {
HttpSessionImpl session = sessions.get(sessionId);
if (session == null) {
// Session未找到,创建一个新的Session:
session = new HttpSessionImpl(this.servletContext, sessionId, inactiveInterval);
sessions.put(sessionId, session);
} else {
// Session已存在,更新最后访问时间:
session.lastAccessedTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
return session;
}
// 删除Session:
public void remove(HttpSession session) {
this.sessions.remove(session.getId());
}
}
SessionManager由ServletContextImpl持有唯一实例。
再编写一个HttpSession的实现类HttpSessionImpl:
public class HttpSessionImpl implements HttpSession {
ServletContextImpl servletContext; // ServletContext
String sessionId; // SessionID
int maxInactiveInterval; // 过期时间(s)
long creationTime; // 创建时间(ms)
long lastAccessedTime; // 最后一次访问时间(ms)
Attributes attributes; // getAttribute/setAttribute
}
然后,我们分析一下用户调用Session的代码:
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
session.invalidate();
由于HttpSession是从HttpServletRequest获得的,因此,必须在HttpServletRequestImpl中引用ServletContextImpl,才能访问SessionManager:
public class HttpServletRequestImpl implements HttpServletRequest {
// 引用ServletContextImpl:
ServletContextImpl servletContext;
// 引用HttpServletResponse:
HttpServletResponse response;
@Override
public HttpSession getSession(boolean create) {
String sessionId = null;
// 获取所有Cookie:
Cookie[] cookies = getCookies();
if (cookies != null) {
// 查找JSESSIONID:
for (Cookie cookie : cookies) {
if ("JSESSIONID".equals(cookie.getName())) {
// 拿到Session ID:
sessionId = cookie.getValue();
break;
}
}
}
// 未获取到SessionID,且create=false,返回null:
if (sessionId == null && !create) {
return null;
}
// 未获取到SessionID,但create=true,创建新的Session:
if (sessionId == null) {
// 如果Header已经发送,则无法创建Session,因为无法添加Cookie:
if (this.response.isCommitted()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot create session for response is commited.");
}
// 创建随机字符串作为SessionID:
sessionId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
// 构造一个名为JSESSIONID的Cookie:
String cookieValue = "JSESSIONID=" + sessionId + "; Path=/; SameSite=Strict; HttpOnly";
// 添加到HttpServletResponse的Header:
this.response.addHeader("Set-Cookie", cookieValue);
}
// 返回一个Session对象:
return this.servletContext.sessionManager.getSession(sessionId);
}
@Override
public HttpSession getSession() {
return getSession(true);
}
...
}
对HttpServletRequestImpl的改造主要是加入了ServletContextImpl和HttpServletResponse的引用:可以通过前者访问到SessionManager,而创建的新的SessionID需要通过后者把Cookie发送到客户端,因此,在HttpConnector中,做相应的修改如下:
public class HttpConnector implements HttpHandler {
...
@Override
public void handle(HttpExchange exchange) throws IOException {
var adapter = new HttpExchangeAdapter(exchange);
var response = new HttpServletResponseImpl(adapter);
// 创建Request时,需要引用servletContext和response:
var request = new HttpServletRequestImpl(this.servletContext, adapter, response);
// process:
try {
this.servletContext.process(request, response);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
当用户调用session.invalidate()时,要让Session失效,就需要从SessionManager中移除:
public class HttpSessionImpl implements HttpSession {
...
@Override
public void invalidate() {
// 从SessionManager中移除:
this.servletContext.sessionManager.remove(this);
this.sessionId = null;
}
...
}
最后,我们还需要实现Session的自动过期。由于我们管理的Session实际上是以Map<String, HttpSession>存储的,所以,让Session自动过期就是定期扫描所有的Session,然后根据最后一次访问时间将过期的Session自动删除。给SessionManager加一个Runnable接口,并启动一个Daemon线程:
public class SessionManager implements Runnable {
...
public SessionManager(ServletContextImpl servletContext, int interval) {
...
// 启动Daemon线程:
Thread t = new Thread(this);
t.setDaemon(true);
t.start();
}
// 扫描线程:
@Override
public void run() {
for (;;) {
// 每60秒扫描一次:
try {
Thread.sleep(60_000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
break;
}
// 当前时间:
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 遍历Session:
for (String sessionId : sessions.keySet()) {
HttpSession session = sessions.get(sessionId);
// 判断是否过期:
if (session.getLastAccessedTime() + session.getMaxInactiveInterval() * 1000L < now) {
// 删除过期的Session:
logger.warn("remove expired session: {}, last access time: {}", sessionId, DateUtils.formatDateTimeGMT(session.getLastAccessedTime()));
session.invalidate();
}
}
}
}
将HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse与Cookie相关的实现方法补全,我们就得到了一个基于Cookie的HttpSession实现!
最后需要注意的一点是,和HttpServletRequest不同,访问HttpServletRequest实例的一定是一个线程,因此,HttpServletRequest的getAttribute()和setAttribute()不需要同步,底层存储用HashMap即可。但是,访问HttpSession实例的可能是多线程,所以,HttpSession的getAttribute()和setAttribute()需要实现并发访问,底层存储用ConcurrentHashMap即可。
测试HttpSession
访问IndexServlet,第一次访问时,将获取到新的HttpSession,此时,HttpSession没有用户信息,因此显示登录表单:
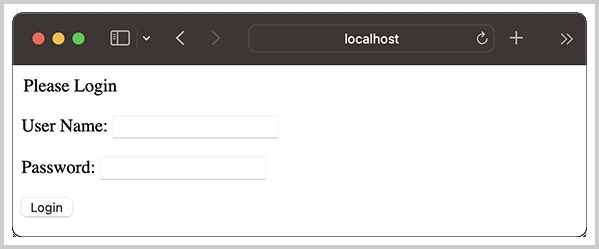
登录成功后,可以看到用户名已放入HttpSession,IndexServlet从HttpSession获取到用户名后将用户名显示出来:
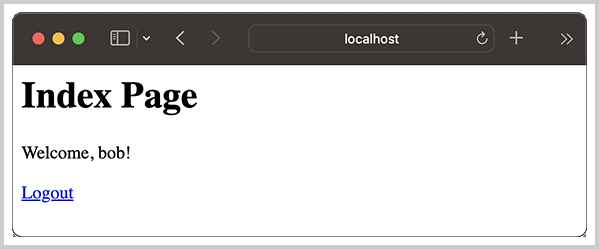
刷新页面,IndexServlet仍将显示登录的用户名,因为根据Cookie拿到相同的SessionID后,获取的HttpSession是同一个实例。
由于我们设定的HttpSession过期时间是10分钟,等待至少10分钟,观察控制台输出:
21:41:38.001 [HTTP-Dispatcher] INFO c.i.j.engine.filter.LogFilter -- GET: /
21:42:05.586 [HTTP-Dispatcher] INFO c.i.j.engine.filter.LogFilter -- GET: /
21:52:15.578 [Thread-0] WARN c.i.j.engine.SessionManagerImpl -- remove expired session: 899eb456-5aa3-40d4-8c64-ddc97d39c0d2, last access time: Fri, 14 Jul 2023 13:42:05 GMT
大约在21:52:15时清理了过期的Session,最后一次访问时间是21:42:05(注意时间需要经过时区调整),再次刷新页面将显示登录表单:

参考源码
小结
使用Cookie模式实现HttpSession时,需要实现一个HttpSessionManager,它在内部维护一个Session ID到HttpSession实例的映射;
HttpSessionManager通过定期扫描所有HttpSession,将过期的HttpSession自动删除,因此,Session自动失效的时间不是特别精确;
由于没有对HttpSession进行持久化处理,重启服务器后,将丢失所有用户的Session。如果希望重启服务器后保留用户的Session,则需要将Session数据持久化到文件或数据库,此功能要求用户放入HttpSession的Java对象必须是可序列化的;
因为Session不容易扩展,因此,大规模集群的Web App通常自己管理Cookie来实现登录功能,这样,将用户状态完全保存在浏览器端,不使用Session,服务器就可以做到无状态集群。